About Us
Conference Mind organization warmly welcomes you all to the Global Meet on “Clinical and Medical Case Report” as International Webinar. “Clinical Meet 2022” is one of the well-established conferences among Pharmaceutical Conferences organized by our organization.
Theme: The Clinical Excellence
Clinical Meet 2022 team aims are to gather all the Professors, Doctors, YRF researchers, Student Researchers and Analyst, Health-Care Professionals, President, Founders, CEOs, Health Care Business Delegates, Business Researchers, Clinical Scholastic, Pharmaceutical Experts, Pharmaceutical Industries and people in the field of Clinical and Medical Case Report for rapid dissemination of scientific knowledge for the future development.
Track 1. Clinical Research:
Clinical research refers to all research carried out on humans (healthy or sick people). It focuses on improving knowledge of diseases and developing diagnostic methods and new treatments or medical devices to ensure better patient care. Below are descriptions of some different kinds of clinical research.
- Treatment Research.
- Prevention Research
- Diagnostic Research
- Screening Research
- Quality of Life Research
- Genetic studies
- Epidemiological studies
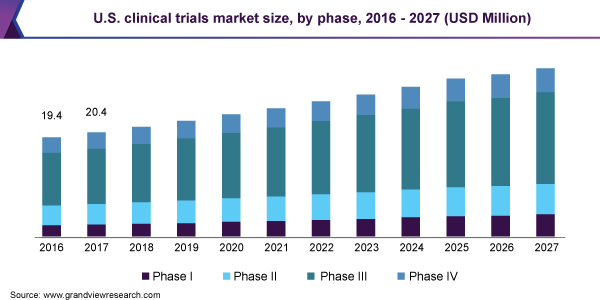
Phases of clinical trials: when clinical research is used to evaluate medications and devices. Clinical trials are often conducted in four phases. The trials at each phase have a different purpose and help scientists answer different questions.
- Phase I trials
- Phase II trials
- Phase III trials
- Phase IV trials are called the final trial.
Track 2. Autopsy:
Autopsy, also called necropsy, postmortem, or postmortem examination, dissection and examination of a dead body and its organs and structures. An autopsy may be performed to determine the cause of death, observe the effects of a disease, and establish the evolution and mechanisms of disease processes.
Track 3. Case Report:
The case report is a specific type of research design that reports on an aspect of the management of one or two patients. It is the first piece of research writing in the health field and represents the most basic type of study design. Health professionals including medical, dental, preventive/epidemiological, nursing and veterinary describe challenging or unusual clinical situations. Mainly not all case reports deal with serious health threats; however, they make a contribution to health knowledge and have educational value or highlight the need for a change in clinical practice or diagnostic/prognostic approaches.
Track 4. Case Studies in Cholera:
Cholera is a classic case study of the interface between the oceans and human health, both in terms of the causes (i.e., a bacterium, copepods, and nutrient pollution of coastal marine waters) and its possible prevention (i.e., the possibility of using in situ moorings and satellites to predict its occurrence). Cholera is a serious intestinal disease that has impacted human health for centuries. This case report demonstrated the infection caused by the bacteria V. cholerae. Its symptoms are vomiting and diarrhoea because of which water loss from the body and dehydration can occur. Due to excessive loss of water from the body, the patient may feel weak and death can also occur, if not cured.
Track 5. Embedding Care Management:
The goals of embedded case management programs are to effectively manage all aspects of care for high-risk, high-cost, complex patients, while also working to reduce hospitalizations and unnecessary costs, assure patient satisfaction, and improve the patient's quality of life. At the point of care or behind the scenes, care coordination by healthcare case managers helps to elevate clinical, quality and financial outcomes in population health management and chronic care, the all-important hallmarks of value-based care.
Track 6. Medical Ontologies for Image Annotation A Case Study:
Creating New Medical Ontologies for Image Annotation focuses on the problem of the medical image’s automatic annotation process, which is solved in an original manner by the authors. All the steps of this process are described in detail with algorithms, experiments and results. The original algorithms proposed by the authors are compared with other efficient similar algorithms.
Track 7. Medical Geology:
Medical Geology looks at the geological factors that affect human, animal and plant health and how we can use natural resources for modern medicine and diagnostics. Medical geology integrates professionals from medicine, geography and geology to handle problems accruing from the geology of an area. Three aspects of geology are relevant for a comprehensive study of health problems arising from the geology of a particular environment, namely mineralogy, geochemistry, and hydrogeology.
Track 8. Clinical Microbiology:
Clinical Microbiology is a study offering diagnostic bacteriology, mycology, parasitology, virology, and mycobacteriology. Clinical microbiology is a specific combination of knowledge, attitude and practice aimed at direct clinical involvement in infectious disease management using the core principles of medical microbiology and clinical medicine. The practices described are the norm in well-organized hospitals. These areas include management of positive blood cultures, management of patients in intensive care units (ICUs), hospital infection control and public health microbiology, development of hospital and community anti-infective policy, and organization of clinical-microbiological meetings and provision of emergency out-of-hours service.
Track 9. Advancements in Psychology Research Methods:
Advancements in Psychology Research Methods encourage the integration of methodological and analytical questions and bring the latest methodological advances to non-methodology experts across all areas of the field. Advancements in Psychology Research Methods Research Practices section includes best practices articles, statistics tutorials, articles on new research tools, commentaries, simulation studies for new techniques, and debates about best practices, among others.
Track 10. Future of Clinical Trials:
Clinical trials are one of the pharmaceutical industry’s most painful and costly processes. Here’s how technology could shape the future of clinical development and transform the trial process from nine years to a matter of hours. Clinical research has benefited from several advancements in recent decades. Expanding access to information has empowered patients to have greater autonomy in their care and a voice during the development process. Personalized medicine has given rise to promising new therapies treating smaller, more targeted populations and the number of clinical trials leveraging virtual health tools and mobile technology is increasing.
The global medical trials market dimension used to be valued at USD 46.8 billion in 2019 and is expected to develop at a compound annual increase rate (CAGR) of 5.1% from 2020 to 2027. Increasing occurrence of persistent sickness and developing demand for scientific trials in growing nations is fueling market growth. Rising quantity of biologics, want for personalized medicines and orphan drugs, and demand for superior technologies are different elements projected to gasoline growth. Factors such as globalization of clinical trials, technological evolution, and demand for Contract Research Organizations (CROs) to conduct clinical trials are in addition projected to drive growth.
The market is additionally driven via the emergence of global pandemic caused by coronavirus. The unexpectedly evolving threat due to the COVID-19 outbreak is impacting lives, communities, businesses, and industries around the world. The pandemic has additionally negatively impacted the current ecosystem of clinical trials. It has affected many ongoing trials for a variety of therapeutic areas. However, to overcome this, researchers are rapidly trying to strengthen innovative therapeutics and vaccines against COVID-19, which is supporting the market growth.
Track 1
Clinical Research
Track 2
Autopsy
Track 3
Case Report
Track 4
Case Studies in Cholera
Track 5
Embedding Care Management
Track 6
Medical Ontologies for Image Annotation A Case Study
Track 7
Medical Geology
Track 8
Clinical Microbiology
Track 9
Advancements in Psychology Research Methods
Track 10
Future of Clinical Trials



